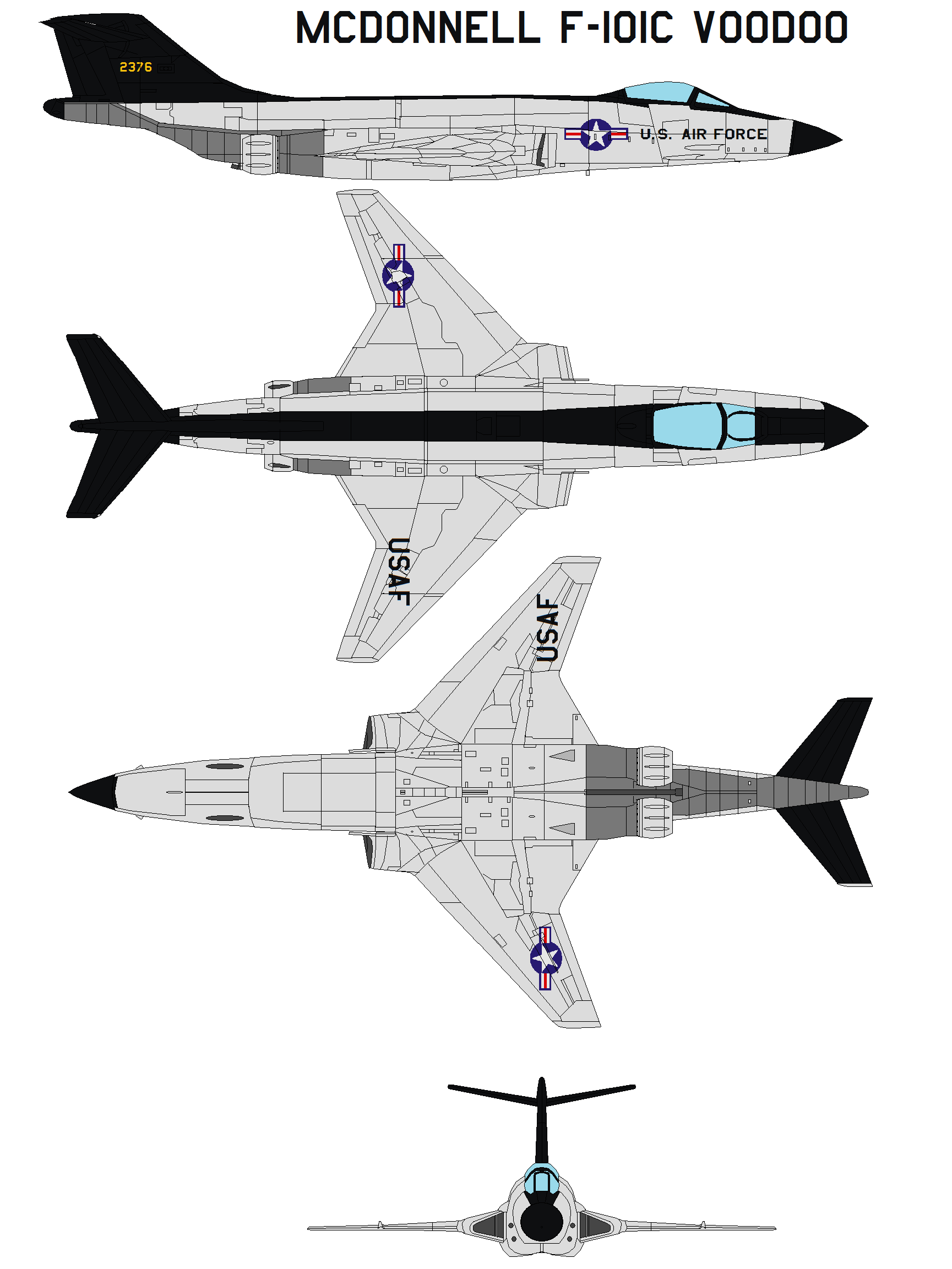
F101 Fighter Jet - The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF).
Originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range escort bomber (known as a penetration fighter) for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command (SAC), the Voodoo was instead developed as a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber for the United States Air Force Tactical Air Command (TAC), and as a photo reconnaissance aircraft based on the same airframe. The F-101A set a number of world jet speed records, including the fastest flying speed ever, reaching 1,207.6 miles (1,943.4 km) per hour on December 12, 1957.
F101 Fighter Jet
Delays in the 1954 interceptor project led to the need for an interim interceptor aircraft design, a role ultimately won by the Model B Voodoo. This required extensive modifications to add a large nose radar, a second crew member to operate it, and a new weapons bay with a revolving door that hid its four AIM-4 Falcon missiles or two AIR-2 Gie missiles. Inside the limbs until it's time to fire. The F-101B entered service with the US Air Force. it. Air Force in 1959 and with the Royal Canadian Air Force in 1961. American samples were transferred to the US Air National Guard, where they served until 1982. Canadian designs remained in service until 1984.
Mcdonnell F 101 F Voodoo Jet Fighter Plane Stock Photo
The career of the Voodoo as a fighter-bomber was relatively short, but the reconnaissance versions lasted for some time. Along with the US Air Force Lockheed U-2 and the US
Interceptor versions served with the Air National Guard until 1982, and in Canadian service they were the front line unit of NORAD until they were replaced by the CF-18 Hornet in the 1980s.
Although the Voodoo was a moderate success, it was arguably more important than an evolutionary step towards being replaced in most roles by the F-4 Phantom II, one of the most successful Western fighters of the 1950s. The Phantom would have retained two engines, a twin interceptor and a tail mounted well above and behind the jet exhaust, but was a development of the F3H Demon while the Voodoo was developed from the earlier XF-88 Voodoo.
The initial design of what would eventually become the Voodoo began immediately after World War II in response to USAAF penetration fighter competition in 1946. It called for a long-range, high-performance fighter to accompany a new generation of bombers, much like the North. The American P-51 Mustang escorted Boeing B-17 Flying Fortresses and Consolidated B-24 Liberators during World War II. Several companies responded with projects, and the Air Force provided funds for some of them to produce prototypes.
F 101 Voodoo Hi Res Stock Photography And Images
After receiving the contract (AC-14582) on February 14, 1947, McDonnell built two prototypes, designated XF-88 Voodoo.
The first prototype (s/n 46-6525), powered by two 3,000 lbf (13.3 kN) Westinghouse XJ34-WE-13 turbojet engines, flew from Murok on 20 October 1948.
Preliminary tests showed that while handling and range were adequate, top speed was a disappointing 641 mph (1,032 km/h) at sea level.
After the installation of McDonnell-designed afterburners on the second prototype, thrust was increased to 3,600 lbf (16.1 kN) with a corresponding increase in top speed, initial rate of climb and reduced takeoff distance. However, the fuel consumption is greatly increased by the use of afterburners, resulting in a reduction in range.
Mcdonnell F 101b Voodoo > National Museum Of The United States Air Force™ > Display
Although the XF-88 won the takeoff competition against the rival Lockheed XF-90 and North American YF-93, the detonation of the first nuclear weapon by the Soviet Union caused the U.S. With at this point, interceptors are more important and bomber escorts are of less priority, and in 1950 he completed the penetration fighter program.
However, analyzes of Korean War missions have shown that modern US it. Air Force strategic bombers are vulnerable to fighter interception. In 1951, the US it. Air Force issued a new requirement for bomber escorts and all major US McDonnell's design was a larger, more powerful version of the XF-88 and won the tender in May 1951. In November 1951, the F-88 was redesignated F-101 Voodoo.
The new design was significantly larger, carried three times the original fuel, and was developed from larger, more powerful Pratt & Whitney J57 turbojets.
The larger size of the J57 Genies required modifications to the gen's compartments and modifications to the air intake to allow more air flow to the gen. New intakes are also designed to be more efficient at higher Mach numbers. To improve aerodynamic efficiency, reduce structural weight, and reduce the pitch effect found during flight testing of the Douglas D-558-2 Skyrocket, an aircraft with a rudder configuration similar to the XF-88, the horizontal tail was modified. moved to the top of the vertical stabilizer, giving the F-101 its distinctive "T-tail". In late 1952, the mission of the F-101 was changed from a "penetration fighter" to a "strategic fighter", which placed equal emphasis on both the task of escorting bombers and delivering nuclear weapons. The new Voodoo mock-up with modified air intake, tail, landing gear and nuclear weapon mock-up was inspected by the Air Force in March 1953.
F 101b \
The project was approved and an initial order for 29 F-101As was placed on 28 May 1953, no prototypes were required as the F-101 was considered a simple development of the XF-88.
With the Cooke-Craigie manufacturing policy, in which initial low-volume production would be used for testing without the use of separate prototypes instead.
F-101A serial number 53-2418 was the first production aircraft; Its first flight was on September 29, 1954 at Edwards AF, where it reached speed 0.9 (960 km/h) at 35,000 feet (11,000 m).
The privately owned aircraft was moved to the Evergreen Maintenance Center in Maran, Arizona, and is now on display at the Evergreen Air and Space Museum in McMinnville, Oregon.
Mcdonnell F 101c Voodoo By Bagera3005 On Deviantart
The end of the Korean War and the development of the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress jet aircraft eliminated the need for fighter escort, and Strategic Air Command withdrew from the program.
Despite the loss of SAC interest, the aircraft caught the attention of Tactical Air Command (TAC) and the F-101 was reconfigured as a fighter-bomber designed to use a single nuclear weapon to destroy tactical targets such as airfields. With TAC support, testing was resumed and Category II flight testing began in early 1955. During development, a number of problems were identified, many of which were eliminated. The plane had a dangerous tendency to pull away sharply at high angles of attack, which was never finally resolved.
Some 2,300 improvements were made to the aircraft in 1955-1956 before full production resumed in November 1956.
The first F-101A was delivered on May 2, 1957 to the 27th Strategic Fighter Wing, which was transferred to TC in July of that year.
Mcdonnell F 101 \
Provides good acceleration, climb, ease of breaking the sound barrier in straight flight and a maximum performance of Mach 1.52. The large internal fuel capacity of the F-101 allowed it to fly approximately 3,000 miles (4,828 km) non-stop.
The aircraft was equipped with the MA-7 fire control radar for both air and mid-air use, and a low-altitude bombing system (LABS) for nuclear weapon delivery.
And was designed to carry the Mk 28 nuclear bomb.. The initial payload for the F-101A was the McDonnell Model 96 Depot, a large fuel/weapons pod similar in concept to the Convair B-58 Hustler but abandoned in March 1956 until How the F-101 stopped serving. Other nuclear payloads included MK 7, MK 43 and MK 57 weapons.
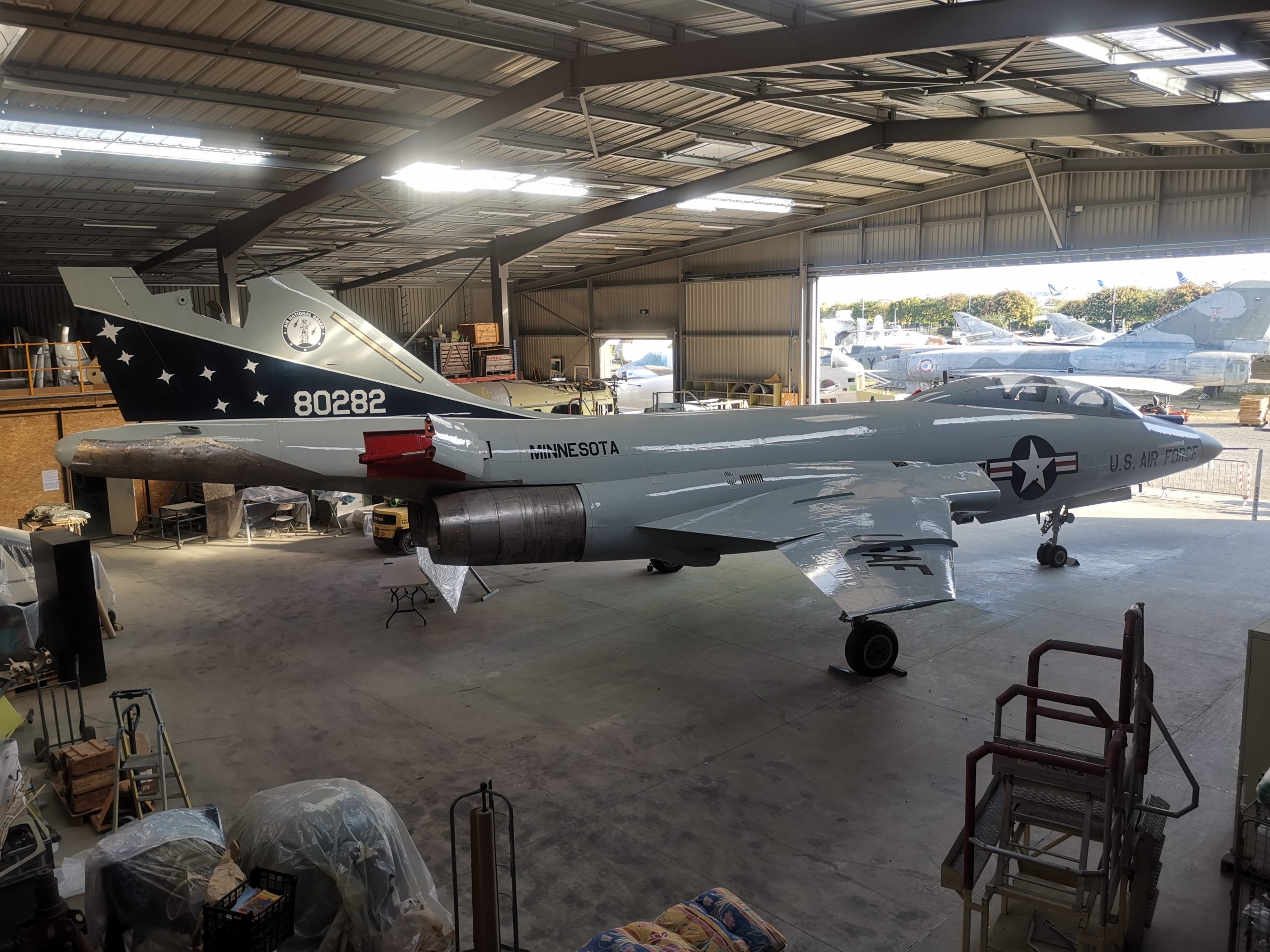

It was fitted with four 20mm M39 cannons, with one cannon often removed in service to make room for the TACAN beacon receiver.
File:f 101 Fighter.jpg
The F-101 set a number of speed records, including: JF-101A (the ninth F-101A, modified as a testbed for the more powerful J-57-P-53 F-101B engines), which set a world speed Record at 1,207.6 mph (1,943.4 km/h) on December 12, 1957 during Operation Firewall,
Beating the previous record of 1,132 mph (1,811 km/h) set by the Fairy Delta 2 last March. The record was subsequently set in May 1958 by the Lockheed F-104 Starfighter. On November 27, 1957, during Operation Sun Run, the RF-101C set the Los Angeles-New York-Los Angeles record at 6 hours 46 minutes, the New York to Los Angeles record at 3 hours 36 minutes, and the record flight time of Los Angeles to New York is 3 hours 7 minutes.
29 survivors were converted to RF-101G specifications with a redesigned nose to house reconnaissance cameras instead of guns and radars. They served in the Air National Guard until 1972.
33rd Task Force RF-101A (s/n 54-1512) after landing at Udorn Royal Thai Air Force Base (later transferred to Tan Son Nhut Air Base) c. 1965
F 101b Voodoo
In October 1953, the US They were followed by 35 production aircraft RF-101A.
The RF-101A shared the airframe of the F-101A, including its 6.33 g (62 m/s²).
Ngad fighter jet, lego fighter jet, fighter jet canvas, the newest fighter jet, fighter jet games, fighter jet toys, f101 fighter, fighter jet training, f101 jet, fighter jet party supplies, latest us fighter jet, f 15 fighter jet


0 Comments